Dieser Beitrag ist auch verfügbar auf:
Deutsch

Egal ob Alkohol, Marihuana, Kokain, Crystal Meth oder sogar Zucker, Salz und Fett: Ab einer gewissen Dosis lösen sie eine erhöhte Ausschüttung von Dopamin aus, eines Botenstoffs, der das Belohnungszentrum anheizt.
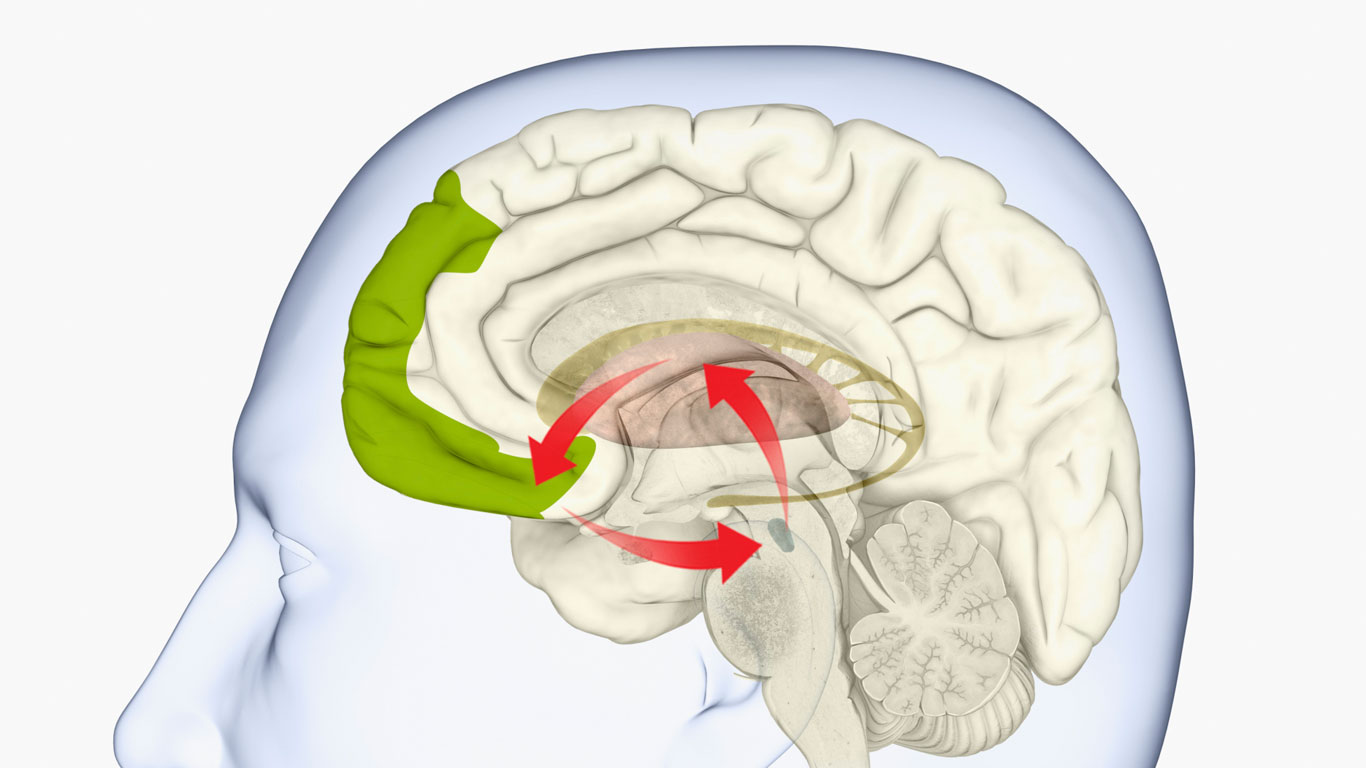
Eine Studie konnte belegen, dass die Dopaminausschüttung beim Essen von zucker-, salz- oder fetthaltiger Nahrung um 50 Prozent ansteigt. Doch im Vergleich zu anderen Stoffen ist dieser Anstieg moderat: Marihuana erhöht die Menge des Glücksstoffs um 175 Prozent, Crystal Meth sogar um 1000 Prozent.
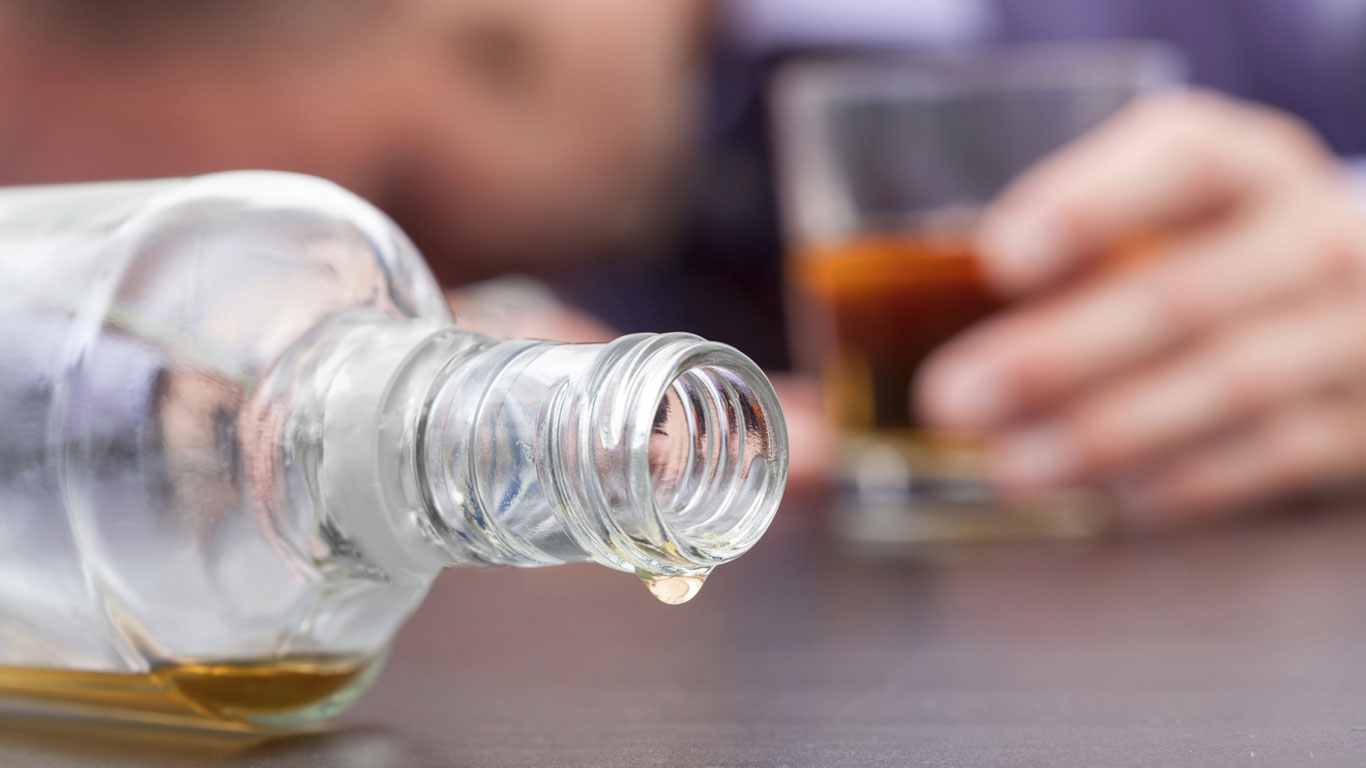

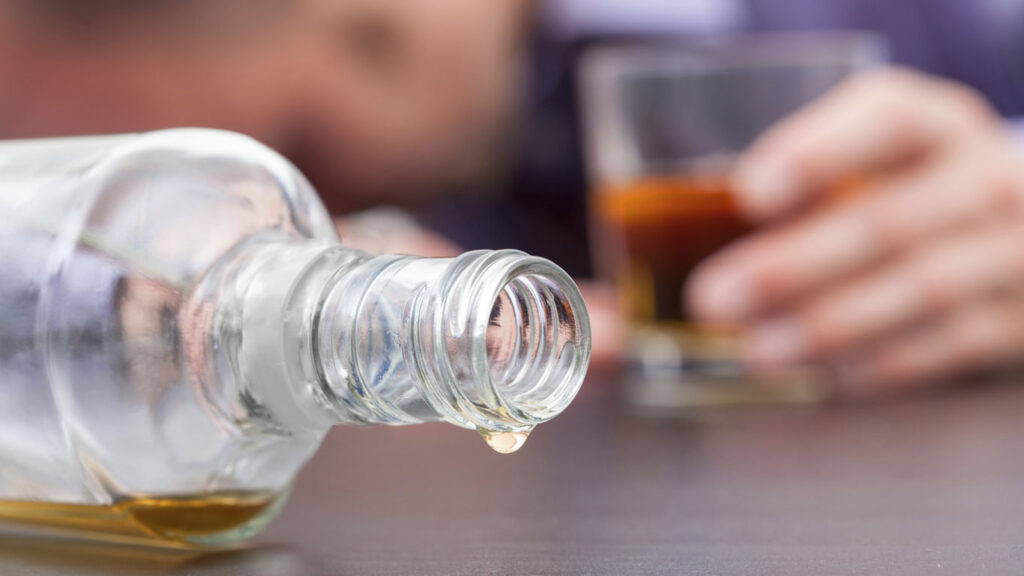
Der kalte Entzug, auch Cold Turkey genannt, ist die radikalste und riskanteste Methode, um clean zu werden. Im Fall einer Alkoholsucht verändert die Droge gleich mehrere Botensysteme im Gehirn. Kappt man nun den Nachschub an Alkohol von einem Moment auf den anderen, senden verschiedene Rezeptoren unentwegt Alarmsignale aus – unser Körper gerät in einen dauerhaften und gefährlichen Stresszustand.
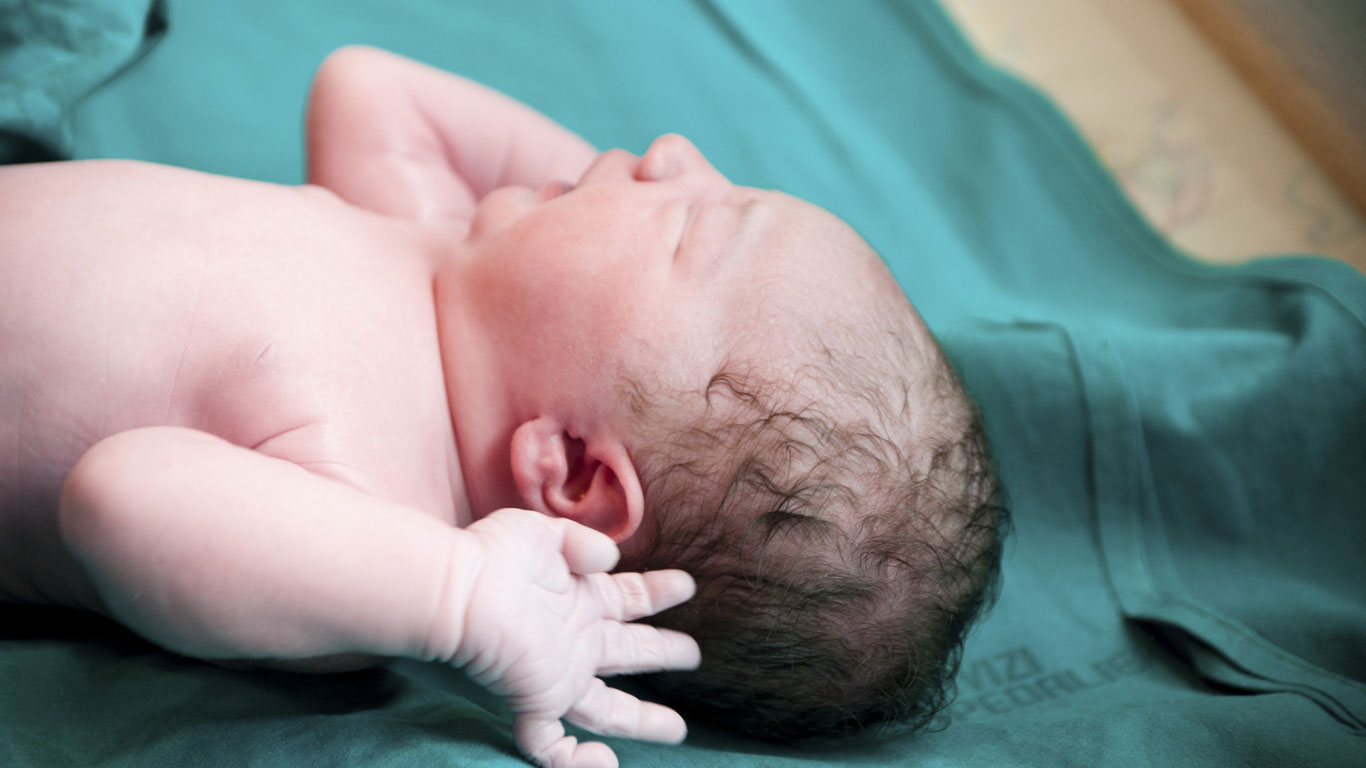
Auf den Neugeborenenstationen in den Kliniken Deutschlands gibt es Hunderte Babys, die auf Entzug sind. Ihr Gehirn wurde durch die von ihren Müttern eingenommenen Drogen schon vor der Geburt auf bestimmte Stoffe abgerichtet. Auch sie müssen peu à peu mit Medikamenten von ihrer angeborenen Sucht geheilt werden.
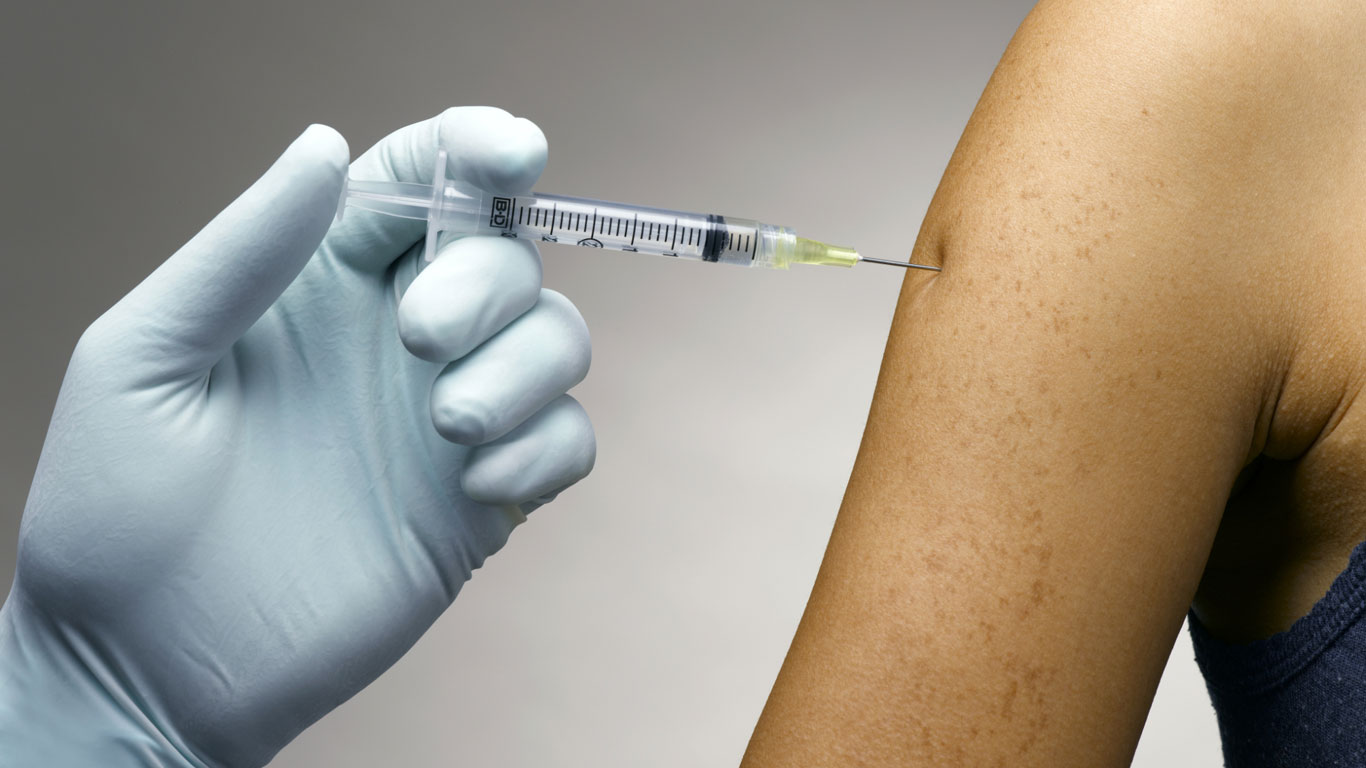
Amerikanische Forscher haben einen Impfstoff gegen Kokain entwickelt. Menschen, die mit dem Stoff geimpft werden, bilden Antikörper gegen Kokain. Die binden sich an das Kokain und sorgen dafür, dass die Droge nicht mehr ins Gehirn eindringen kann. Folge: Der Rausch bleibt aus – der Mensch verlernt, nach mehr zu verlangen.
Exactly ten hours ago, a war broke out in Martin Kressner’s body (name changed by the editors). Millions of nerve cells fire without interruption; the brain, muscles and heart are in a state of emergency. His T-shirt is soaked with sweat and the clinical thermometer reads 40 degrees Celsius.
At the same time, the intensity of the hallucinations increases from minute to minute. He sees a fighter jet speeding towards him in his living room. He notices how his body begins to tremble, his muscles spasm uncontrollably. Breathing stops and shortly afterwards the heart stops beating. The long-time alcoholic dies, twelve hours after his 42nd birthday.
The paradox: Martin Kressner doesn’t die because he drank too much at once or because his organs collapsed due to the constant consumption of alcohol, on the contrary: he dies because he cut off his alcohol intake from one moment to the next and his body went to war against him. Doctors call this phenomenon delirium tremens – a kind of fatal epileptic seizure in the course of cold turkey. But what exactly happens in our body during withdrawal? What makes us addicted and why? And how long does it take for the organs to regenerate?
Brain hack: Why does my brain crave poison?
Whether it’s alcohol, marijuana, cocaine, crystal meth or even sugar, salt and fat – even if all these substances have very different effects on different parts of the body, they all have one thing in common: from a certain level, they have a negative effect on the body. Dose they trigger an increased release of Dopamine a neurotransmitter that stimulates the reward center. A study has shown that the release of dopamine increases by 50 percent when eating foods high in sugar, salt or fat. However, this increase is moderate compared to other substances.
Marijuana increases the amount of the happy tsunami by 175 percent,
alcohol
by 200 percent, cocaine by 400 percent and crystal meth by as much as 1000 percent. The effects of this physical state of emergency are precisely comprehensible: Due to the increased release, more nerve cells respond to the corresponding drug.
And the more nerve endings are available for the molecules to dock onto, the more positive the good feeling is rated. All the toxins that flow into our body with the substances then no longer play a role for the brain. It has long been in self-destruct mode.
“Drugs behave in a similar way to Trojans. They hack into the brain and into neuronal connections that are actually intended for completely different things such as food intake,” says Prof. Dr. Jens Reimer, Head of the Center for Interdisciplinary Addiction Research at the University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf (UKE). In this way, a so-called addiction memory is formed. From now on, the more frequent the consumption, the more difficult it is to delete. If you try it anyway, it can end fatally …
Cold Turkey: What happens if my brain is put on instant withdrawal?
Martin Kressner had to die because he overestimated his body – and chose a form of detoxification that most doctors now strongly advise against: cold turkey. “It is the most radical and risky method to get clean,” says addiction specialist Jens Reimer from the UKE. But what exactly makes this withdrawal so unpredictable – and under certain circumstances even fatal?
“We refer to alcohol as a dirty drug. This is because alcohol alters several different messenger systems in the brain,” explains Reimer. If the supply of alcohol is cut off from one moment to the next, various receptors (including the so-called GABA and NMDA receptors) constantly send out alarm signals; with heroin, for example, only one type of receptor fires. As a result, the person affected becomes so stressed during cold turkey that their body collapses under the strain and their cardiovascular system collapses.
Red alert and full throttle
Alcohol has a sedative effect, especially in higher doses. Chronic consumption is like constant pressure on the brake pedal. If the alcohol suddenly stops, there is no brake and the body goes full throttle. The risk of this delirium tremens only decreases after a few days, when the receptors have become accustomed to the situation and reduce their neurotransmitter fireworks.
Addiction researchers such as Prof. Reimer therefore recommend a gradual withdrawal from alcohol or other drugs in the case of severe alcohol addiction, but also in the case of some other severe drug addictions, in which the neurons are slowly weaned off alcohol or other drugs.
This is achieved with the help of medication that imitates part of the effect of the substance to be withdrawn during withdrawal. They weaken the withdrawal symptoms such as tremors, fever and muscle cramps. Depending on the drug and the duration of the addiction, this can take days or even weeks. For some patients, however, this withdrawal therapy does not begin after years of drug addiction, but only 24 hours after the first breath …
Finnegan scores: Is there a guide to withdrawal?
The blindfolds are tight, no light or sound reaches them, the withdrawal patients lie almost motionless in their beds. What distinguishes them from other drug addicts is that they have never had a sip of alcohol, snorted cocaine or pushed heroin in their lives – because they are only a few days old. In fact, there are hundreds of babies in neonatal wards in German hospitals who are in withdrawal. Their brains were trained to use certain substances by the drugs taken by their mothers even before birth.
Withdrawal symptoms occur within 24 to 48 hours after birth. It is the moment when the drug level suddenly drops after nine months of pregnancy, as the newborn is no longer being cared for by the mother. The severity of withdrawal is determined using the so-called Finnegan scores, tables that indicate which dose is administered for which symptoms.
Shrill screams, fever, seizures – the withdrawal symptoms are similar to those of many adult addicts. In order to alleviate the symptoms, this is also done step by step. Newborn babies are given morphine drops in their mouths every four to six hours. Withdrawal lasts up to four weeks.
Search areas on stand-by
But no matter what age the addict is: The craving, i.e. the brain’s irrepressible desire for drugs, cannot be completely switched off by these drugs, neither with alcohol nor with heroin, cocaine or crystal meth. Depending on the drug, it may take days, weeks or months for the physical withdrawal symptoms to subside.
In addition, the addiction memory is far from being erased after this time and usually remains for a lifetime. All it takes is a puff on a cigarette, a shot of heroin or a drop of alcohol years later to reactivate it. Addiction researchers refer to these post-withdrawal patients as “wet consumers”. Although they are physically sober and have banished the drug itself from their bodies, certain addiction areas in the brain are still in sleep mode and are just waiting to be woken up.
Dr. Zombie: Can you get clean in 20 minutes?
Patrick Lutz (name changed by the editors) is desperate. Heroin has dominated his life for years. He has gone through 13 withdrawals, all of which have failed. Each time, his will was too weak, his stamina too low to go through the weeks of withdrawal. Now he is betting everything on one card, or rather on one man: Dr. Michail Zobin – also known as Dr. Zombie.
In his clinic in Moscow, the military doctor offers what is said to be the most successful heroin therapy in the world. There’s just one catch: if you relapse, you die immediately. Lutz is lying on a table, infusions and tubes stuck in his body. Zobin does not provide any information about what exactly happens next.
The doctor injects a milky fluid into a vein in the patient’s neck. “A messenger substance that blocks the receptors,” says Zobin. Like a seal on a tooth, the substance is supposed to close the addiction memory forever. The procedure is completed after 20 minutes. Shortly afterwards, Lutz falls into a long sleep. The next morning he feels no desire for a shot, the craving symptoms seem to have been extinguished.
Forever clean or dead immediately
In Zobin’s clinic, the test is finally put to the test. The doctor injects the Swiss man with an opiate 40 times weaker than heroin. If the receptor sealing was successful, the injection acts like an overdose. And indeed: Lutz’s breathing stops, he would die – if Zobin didn’t give him artificial respiration. The experiment shows that if Lutz were to inject himself, he would die of an overdose.
Many doctors criticize Zobin’s treatment, saying it makes no sense from a scientific point of view, while others consider him a fraud. Zobin’s figures speak a different language. According to the study, only one percent of all patients relapse (i.e. die). By comparison, the relapse rate for conventional heroin withdrawal programs is around 90 percent. Today, three years after treatment, Patrick Lutz is still clean.
Drug blockers: is there a vaccination against cocaine?
But what if you don’t want to put your life in the hands of a Moscow military doctor? And what if you are addicted to a drug for which there is no substitute during withdrawal? Like cocaine, for example? Thomas Kosten and his colleagues at Weill Cornell Medical College in New York have been looking for other solutions – and have recently found what they were looking for: They have developed a vaccine against cocaine.
In fact, people who are inoculated with the substance form antibodies against cocaine. These bind to the cocaine and ensure that the drug can no longer penetrate the brain. Like a virus blocker in a PC, the vaccine gives cocaine no chance and intercepts it before the substance can manipulate the reward center.
The result: the high doesn’t come – people forget to crave more. Over the past five years, the researchers have vaccinated more than 400 cocaine addicts. The vaccination was effective in 75 percent of cases. A value that gives hope to millions of people …






